Port strike 2024: Map of affected locations, product impacts, updates

Dockworkers strike threatens US supply chain
Thousands of dockworkers from Maine to Texas have gone on strike, demanding a pay raise and fair working conditions. The strike threatens to disrupt the U.S. supply chain and could cost the economy more than $4 billion a day.
NEW YORK - UPDATE: According to the Associated Press, a deal to suspend the strike until January 15 has been reached.
Around 45,000 dockworkers at 36 ports across the East Coast, including New York/New Jersey, are now on strike.
ILA STRIKE 2024 UPDATE TODAY: MAP l IMPACTS l HOLIDAY SHOPPING
***Click each headline to jump to the designated topic.
Workers began walking picket lines early Tuesday in a strike over wages and the ports’ use of automation. The contract between U.S. Maritime Alliance, which represents the ports, and thousands of members of the International Longshoremen’s Association expired.
Featured
Port strike 2024: Which products could face shortages, price hikes?
If drawn out, the strike would force businesses to pay shippers for delays and cause some goods to arrive late for peak holiday shopping season.
The strike, which impacts port operations from Maine to Texas, could snarl supply chains, and if it stretches on for more than a few weeks, the work stoppage could lead to shortages and higher prices for American consumers.
Port worker strike: Which ports are affected?
While any port can handle any type of goods, some ports specialize in handling goods for a particular industry.
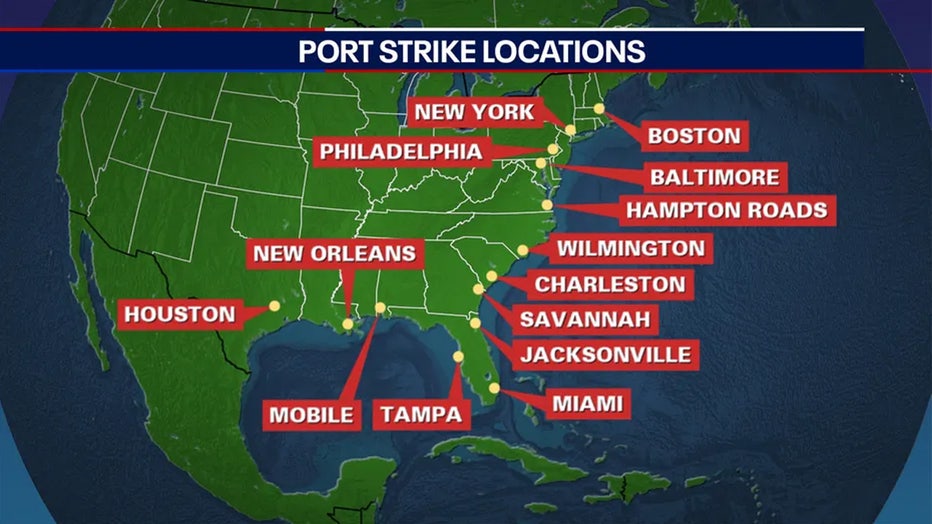
Those affected by the shutdown include:
- Baltimore and Brunswick, Georgia (the top two busiest auto ports)
- Philadelphia, which gives priority to fruits and vegetables
- New Orleans, which handles coffee, mainly from South America and Southeast Asia, various chemicals from Mexico and North Europe, and wood products such as plywood from Asia and South America.
Other major ports affected include:
- Boston
- New York/New Jersey
- Norfolk, Virginia
- Wilmington, North Carolina
- Charleston, South Carolina
- Savannah, Georgia
- Tampa, Florida
- Mobile, Alabama
- Houston
ILA strike: What about West Coast ports?
Dockworkers at West Coast ports are represented by a different union, so they are not currently on strike.
But since the work stoppage is impacting East Coast operations, many shipments could be rerouted out West, potentially creating traffic jams.

Dockworkers strike hits over 30 US ports
Dockworkers are officially on strike. The strike affects over 30 ports from Maine to Texas. It's the first of its kind in decades after the contract between the ports and union members expired at midnight. FOX 5 NY's Duarte Geraldino has the latest.
Railroads have also said they can ramp up to carry more freight from the West Coast, but analysts say they can’t move enough to make up for the closed Eastern ports.
The congestion will likely cause delays, and pressure on demand could mean higher costs for businesses.
Update on port strike: Why is it happening?
The International Longshoremen’s Association is demanding significantly higher wages and a total ban on the automation of cranes, gates and container-moving trucks that are used in the loading or unloading of freight at 36 U.S. ports. Those ports handle roughly half of the nations’ cargo from ships.
The contract between the ILA and the United States Maritime Alliance, which represents the ports, expired Tuesday. Some progress was reported in talks late Monday, but the union went on strike anyway.
Featured
Port strike 2024 triggers toilet paper 'panic buying' at Costco locations
Videos posted online claim that toilet paper is sold out at Costco stores in several states – including New Jersey – with one worker saying their stock was cleared one hour after opening.
The union’s opening offer was for a 77% pay raise over the six-year life of the contract, with President Harold Daggett saying it’s necessary to make up for inflation and years of small raises. ILA members make a base salary of about $81,000 per year, but some can pull in over $200,000 annually with large amounts of overtime.
Monday evening, the alliance said it had increased its offer to 50% raises over six years, and it pledged to keep limits on automation in place from the old contract. The alliance also said its offer tripled employer contributions to retirement plans and strengthened health care options.
How long will the port strike last?
Just how long the strike lasts depends on how severely the supply chain could be affected.
What products will be affected by the port strike?
If drawn out, the strike would force businesses to pay shippers for delays and cause some goods to arrive late for peak holiday shopping season – potentially impacting delivery of anything from toys or artificial Christmas trees, to cars, plywood, coffee, fruit and vegetables.
Americans could also face higher prices as retailers feel the supply squeeze.
"Everyone from the shipping lines to trade groups and maritime industry analysts also warns of widespread ramifications in the global supply chain," reported The Maritime Executive, a maritime industry magazine and newsletter. "Sea-Intelligence has estimated that for each day of a strike, it would take four to six days to clear the backlog. They wrote that even a two-week strike could have ramifications into 2025."
In addition, according to the American Farm Bureau Federation, the affected ports handled 75% of the country's banana imports.
How will a strike affect holiday shopping?
Chris Butler, CEO of National Tree Company in New Jersey, tells the AP that if a strike lasts only a few days, there would still be time to unload Christmas trees, transport them to warehouses, and prepare them for customers this season.
Ships carrying the trees were en route to New York but wouldn't arrive before Tuesday. If the strike continues, Butler warned that most trees would have to be stored until next Christmas season.
Featured
Here's how the port strike could affect the holidays
This holiday season might be a little less merry —with Christmas trees and holiday goods stuck in transit. Experts warn that more than a month could cause product shortages.
If a strike keeps ports closed until November, about 150,000 Christmas trees could miss the peak shopping season, costing National Tree Company and others. In the worst case, these costs could drive inflation and strain the U.S. economy.
A prolonged strike would require companies to compensate shippers for delays, potentially causing goods to arrive late for the peak holiday shopping season.




